
The Prime Meridian is set as 0° longitude and it divides the Earth into the Eastern and the Western Hemispheres. This line is also known as the Prime Meridian. Today, the meridian line through Greenwich, England, is considered as the reference point for longitudes. However, in order to measure the position of a location based on the longitude, cartographers and geographers over the course of history have designated different locations as the main longitudinal reference point. Unlike, latitudes, there is no obvious central longitude. Meridians are perpendicular to every latitude. Half of a longitudinal circle is known as a Meridian. Longitudes are, therefore, imaginary circles that intersect the North and South Poles and the Equator. On a map where north is up, longitudes run vertically. They meet at both Poles and specify the east-west position of a location. Longitudes are geographical positioning markers that run from the geographical North Pole to the geographical South Pole, intersecting the Equator. This eliminates the need to add whether the specified latitude is north or south of the Equator. Latitudes south of the Equator are given negative values. Sometimes, latitudes north of the Equator are denoted by a positive sign. It is the southern-most position on the globe, where the Sun is directly overhead during the December Solstice. The Tropic of Capricorn is the latitude that lies at 23° 26′ South of the Equator. This happens during the June Solstice, when the Earth’s Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun. It marks the northern-most position on the Earth, where the Sun is directly overhead at least once a year. The latitude 23° 26′ North is also known as the Tropic of Cancer. Places in both the Arctic and Antarctic circles experience the Midnight Sun and polar night. Any locations falling south of this latitude are said to be in the Antarctic Circle.
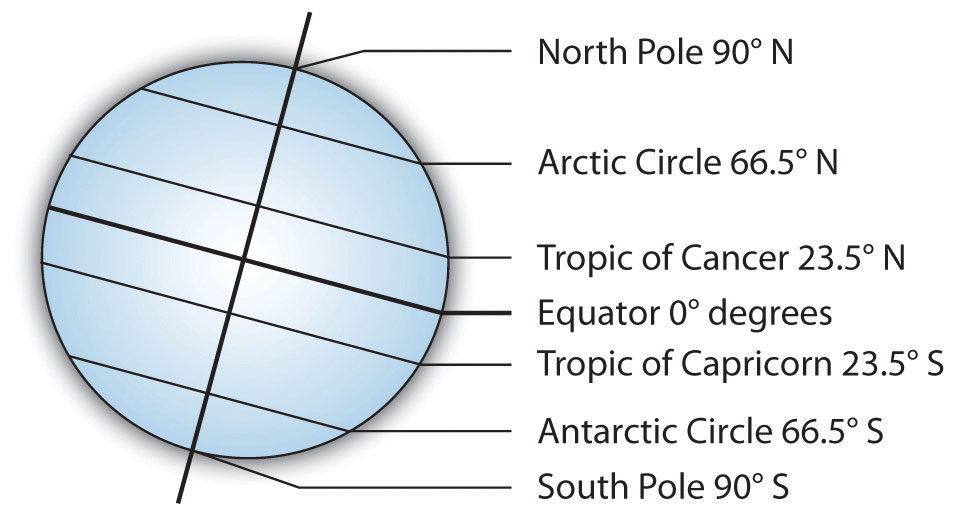
The Arctic Circle is the latitude 66° 34′ North. The positions of these latitudes are determined by the Earth's axial tilt. In addition to the Equator, there are four other major latitudes that are usually found on maps and globes. The Equator represents 0° latitude, while the North and South Poles represent 90° North and 90° South latitudes. Southern Hemisphere locations, on the other hand, are on southern latitudes and are assigned a suffix of S for south.įind celestial objects in the sky Notable Latitudes Locations in the Northern Hemisphere are identified by northern latitudes and are assigned a suffix of N for north. Latitudes specify the north-south position of a location on the globe. They are named after the angle created by a line connecting the latitude and the center of the Earth, and the line connecting the Equator and the center of the Earth. On a map where north is up, latitudes run laterally (left to right). Often called parallels or circles of latitude, latitudes are imaginary circles parallel to the Equator. The Equator passes through 14 countries, including Uganda, Kenya, Somalia, Indonesia, Ecuador, Colombia, and Brazil. On the Equinoxes – September and March – the Sun is directly overhead the Equator, resulting in almost exactly 12 hour days and 12 hour nights. They also experience at least 12 hours of daylight every day during the year.

Most locations on the Equator experience consistently high temperatures throughout the year. It is equidistant from the North and South Poles, and divides the globe into the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. The Equator is an imaginary line perpendicular to this axis.

If we draw a line passing through the center of the Earth along its rotational axis, the line would pass through the North and the South Pole. Scientists call this shape a spheroid or ellipsoid. The Earth is, almost, but not quite, a sphere that rotates around its axis. Both latitudes and longitudes are measured in degrees (°) and minutes (′).Īstronomical terms & definitions Dividing Earth Into Hemispheres Together, they form the Earth’s geographical coordinates, and represent the angular distance of any location from the center of the Earth. Business Date to Date (exclude holidays).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
